

- #CUT OFF WAVELENGTH OF SINGLE MODE FIBER HOW TO#
- #CUT OFF WAVELENGTH OF SINGLE MODE FIBER SOFTWARE#
- #CUT OFF WAVELENGTH OF SINGLE MODE FIBER FREE#
From eq.(1), at the operating wavelength less than cut-off wavelength the V-number exceeds 2.405. More than one propagation mode in the optical fiber can be found with the V-number greater than 2.405. The number of propagation mode in the optical fiber depend on the V-number. IV.Single mode fiber R ESULTS AND D ISCUSSION. This definition was produced because the first higher order LP11 mode is strongly affected by fiber length and curvature near cutoff. concatenated single mode fiber with different cut-off wavelength.
An effective cutoff wavelength has been defined by the ITU-T which is obtained from a 2 m length of fiber containing a single 14 cm radius loop. Thus for step index fiber where $V_c= 2.405,$ the cutoff wavelength is given by Single-mode operation only occurs above a theoretical cutoff wavelength $λ_c$ given by: Even with the fiber in its straightest condition. The main mechanism by which these weakly guided modes are lost from the core is bending. This occurs as a result of the way the light interacts with the structure of the fiber at a macroscopic level. Therefore, cut-off wavelengths can not always be precisely determined in experiments.I. Cutoff wavelength in an optical fiber is defined as the wavelength above which all but the most strongly guided mode are lost from the core. Therefore, even for moderate bending of the fiber one may obtain sharply increasing propagation losses near the cut-off wavelength. Just below its cut-off wavelength, the bend losses of a mode can become very high due to the increased mode area. In step-index fibers, there is no cut-off for the fundamental (LP 01) mode.įor other fiber designs, in particular for some photonic crystal fibers, there can also be a fundamental cut-off.įibers with not radially symmetric designs (and strongly bent fibers) can have polarization-dependent cut-off wavelengths. However, an optical fiber is always able to propagate at.
#CUT OFF WAVELENGTH OF SINGLE MODE FIBER SOFTWARE#
The diagram has been produced with the software RP Fiber Power.įor LP lm modes of a fiber, only for l = 0 the fraction of the power guided in the core goes to zero when approaching the cut-off.įor modes with higher l, the mode size stays finite there. The wavelength at which a mode ceases to propagate is called the cutoff wavelength for that mode.

The thin vertical lines indicate the calculated cut-off wavelengths of the modes. Figure 1:įraction of the power of various guided modes (where the colors are related to the l indices of those) which is contained in the fiber core as a function of the wavelength. Description : At what frequency compared to the cutoff frequency of a. est At what frequency compared to the cutoff frequency of a waveguide will the wavefronts be reflected back and forth across the guide (setting up standing waves) and no energy.
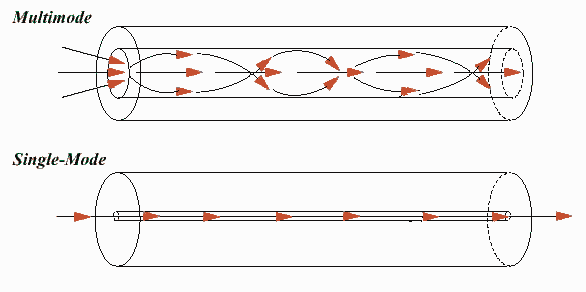
That effect is shown in Figure 1 for a multimode step-index fiber similar behavior occurs for fibers with other transverse refractive index profiles. The cutoff wavelength of which single mode fiber type is more sensitive to length. Typically, the mode radius (and thus the effective mode area) increases sharply near the cut-off, and the fraction of power propagating within the waveguide core decreases accordingly. Just below the cut-off wavelength, the mode properties often vary substantially. The CUTOFF WAVELENGTH of a single-mode fiber is the wavelength above which the fiber propagates only the fundamental mode. When a particular mode ceases to exist beyond a certain wavelength, that wavelength is called its cut-off wavelength.įor an optical fiber, the cut-off wavelength for the LP 11 mode sets a limit to the single-mode regime, as below that wavelength there is at least the LP 01 and the LP 11 mode. The number of guided modes of a waveguide (for example, an optical fiber) depends on the optical wavelength: the shorter the wavelength, the more modes can be guided.įor long wavelengths, there may be only a single guided mode (→ single-mode fibers) or even none at all, whereas multimode behavior is obtained at shorter wavelengths.
#CUT OFF WAVELENGTH OF SINGLE MODE FIBER HOW TO#
How to cite the article suggest additional literature
#CUT OFF WAVELENGTH OF SINGLE MODE FIBER FREE#
Encyclopedia > letter C > cut-off wavelength Cut-off WavelengthĬut-off wavelengths and other properties of guided modes can be calculated with our free fiber optics software RP Fiber Calculator.ĭefinition: a wavelength above which a guided mode of a waveguide ceases to exist


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
